Architecture overview
The Dagster+ Hybrid architecture is the most flexible and secure way to deploy Dagster+. It allows you to run your user code in your environment while leveraging Dagster+'s infrastructure for orchestration and metadata management.
Hybrid architecture overview
A hybrid deployment utilizes a combination of your infrastructure and Dagster-hosted backend services.
The Dagster backend services - including the web frontend, GraphQL API, metadata database, and daemons (responsible for executing schedules and sensors) - are hosted in Dagster+. You are responsible for running an agent in your environment.
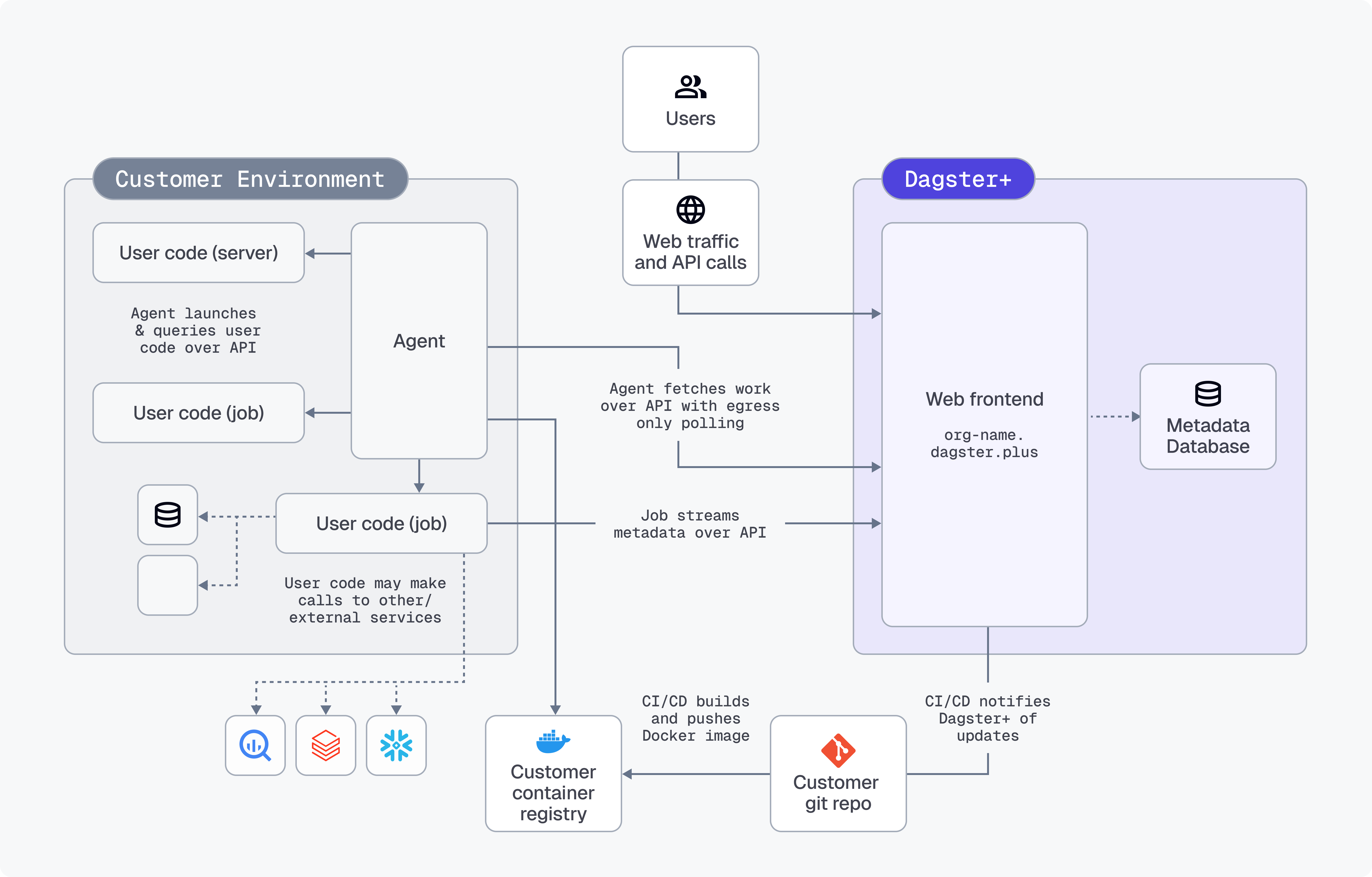
Work is enqueued for your agent when:
- Users interact with the web front end,
- The GraphQL API is queried, or
- Schedules and sensors tick
The agent polls the agent API to see if any work needs to be done, and launches user code in a code server as appropriate to fulfill requests. User code then streams metadata back to the agent API (GraphQL over HTTPS) to make it available in Dagster+.
All user code runs within your environment, in isolation from Dagster system code.
The agent
The Dagster+ agent is a long-lived process that polls Dagster+'s API servers for new work, and launches or queries your user code as needed. Currently, Dagster supports the following agents:
You can also install a local agent to experiment with Dagster+ before deploying a more scalable Hybrid agent, or run multiple agents to provide redundancy if a single agent goes down.
If you're not sure which agent to use, we recommend the Dagster+ Kubernetes agent in most cases.
Infrastructure management
The Dagster+ agent:
- Launches and manages code servers for each code location
- Launches run workers (new containers/processes) when runs need to be executed
- Acts as the run launcher, spinning up isolated tasks/pods/processes for each run
Communication
Additionally, the agent:
- Receives messages and instructions from Dagster+ about what work needs to be done
- Sends metadata back to Dagster+ about launched runs and code server status
Code server
In Dagster+ Hybrid, each code location is served by a long-standing user code server running in your environment. When you inform Dagster+ about a new code location, we enqueue instructions for your agent to launch a new code server. Dagster+ communicates with the code server (through the agent) to:
- Load definitions and metadata (UI browsing, asset graphs)
- Evaluate sensors/schedules (or call into them)
- Launch and monitor runs
- Stream logs and materialization events
Runs
Your definitions might include automations that launch runs or materialize assets. Or your developers might launch runs directly with the web UI.
When a run needs to be launched, Dagster+ enqueues instructions for your agent to launch a new run. The next time your agent polls Dagster+ for new work, it will see instructions about how to launch your run. It will delegate those instructions to your code server and your code server will launch a run - a new run will typically require its own container.
Your agent will send Dagster+ metadata letting us know the run has been launched. Your run's container will also send Dagster+ metadata informing us of how the run is progressing. The Dagster+ backend services will monitor this stream of metadata to make additional orchestration decisions, monitor for failure, or send alerts.
Security
Dagster+ Hybrid relies on a shared security model.
The Dagster+ control plane is SOC 2 Type II certified and follows best practices such as:
- encrypting data at rest (AES 256) and in transit (TLS 1.2+)
- highly available, with disaster recovery and backup strategies
- only manages metadata such as pipeline names, execution status, and run duration
The execution environment is managed by the customer:
- Dagster+ doesn't have access to user code—your code never leaves your environment. Metadata about the code is fetched over constrained APIs.
- All connections to databases, file systems, and other resources are made from your environment.
- The execution environment only requires egress access to Dagster+. No ingress is required from Dagster+ to user environments.
Additionally, the Dagster+ agent is open source and auditable
The following highlights are described in more detail below:
Interactions and queries
When Dagster+ needs to interact with user code - for instance, to display the structure of a job in the Dagster+ user interface, to run the body of a sensor definition, or to launch a run for a job - it enqueues a message for the Dagster+ Agent. The Dagster+ Agent picks up this message and then launches or queries user code running on the appropriate compute substrate.
Depending on the agent implementation, user code may run in isolated OS processes, in Docker containers, in ECS Tasks, in Kubernetes Jobs and Services, or in a custom isolation strategy.
Queries to user code run over a well-defined gRPC interface. Dagster+ uses this interface to:
- Retrieve the names, config schemas, descriptions, tags, and structures of jobs, ops, repositories, partitions, schedules, and sensors defined in your code
- Evaluate schedule and sensor ticks and determine whether a run should be launched
When the agent queries user code, it writes the response back to Dagster+ over a well-defined GraphQL interface.
Runs
Runs are launched by calling the dagster api CLI command in a separate process/container as appropriate to the agent type. Run termination is handled by interrupting the user code process/container as appropriate for the compute substrate.
When runs are launched, the user code process/container streams structured metadata (containing everything that's viewable in the integrated logs viewer in the Dagster+ UI) back to Dagster+ over a well-defined GraphQL interface. Structured metadata is stored in Amazon RDS, encrypted at rest.
By default, the run worker also uploads the compute logs (raw stdout and stderr from runs) to Dagster+. If you don't want to upload logs, you can disable this feature in the agent settings.
Ingress
No ingress is required from Dagster+ to user environments. All network requests are outbound from user environments to Dagster+.
Metadata
The following metadata is stored in the Dagster+ control plane:
Asset definition metadata
| Metadata type | When stored |
|---|---|
| Asset names and keys | Always stored |
| Asset descriptions | Stored if defined |
| Asset dependencies and lineage | Always stored |
Owners (email addresses or team names, like team:data-eng) | Stored if defined |
| Tags (key-value pairs for organization) | Stored if defined |
| Asset groups and partitions definitions | Stored if defined |
| Source code references and links | Stored if defined |
Runtime/materialization metadata
| Metadata type | When stored |
|---|---|
Table metadata (column names, types, and descriptions, via TableSchema and TableColumn objects) | Stored if defined |
Row count (stored under dagster/row_count metadata key) | Stored if defined |
| Column-level lineage (how columns are created and used) | Stored if defined |
Custom metadata -- various MetadataValue types including text, Markdown, JSON, numeric values (automatically plotted over time), URLs, file paths, table schemas, and data previews | Stored if defined |
Run and event metadata
| Metadata type | When stored |
|---|---|
| Run status, timestamps, and execution context | Always stored |
| Asset materialization events | Always stored |
| Output metadata from asset executions | Stored if defined |
| Backfill and partition information | Always stored |
| Job and schedule execution history | Always stored |
Operational metadata
| Metadata type | When stored |
|---|---|
| Code location configurations | Always stored |
| Resource definitions and configurations | Stored if defined |
| Automation conditions and policies | Stored if defined |
| Asset checks and data quality results | Stored if defined |
Key schema fields
| Metadata type | When stored |
|---|---|
dagster/column_schema (table structure metadata) | Stored if defined |
dagster/row_count (row count tracking) | Stored if defined |
| Custom keys for business-specific metadata | Stored if defined |
| Partition keys and time-based metadata | Stored if defined |